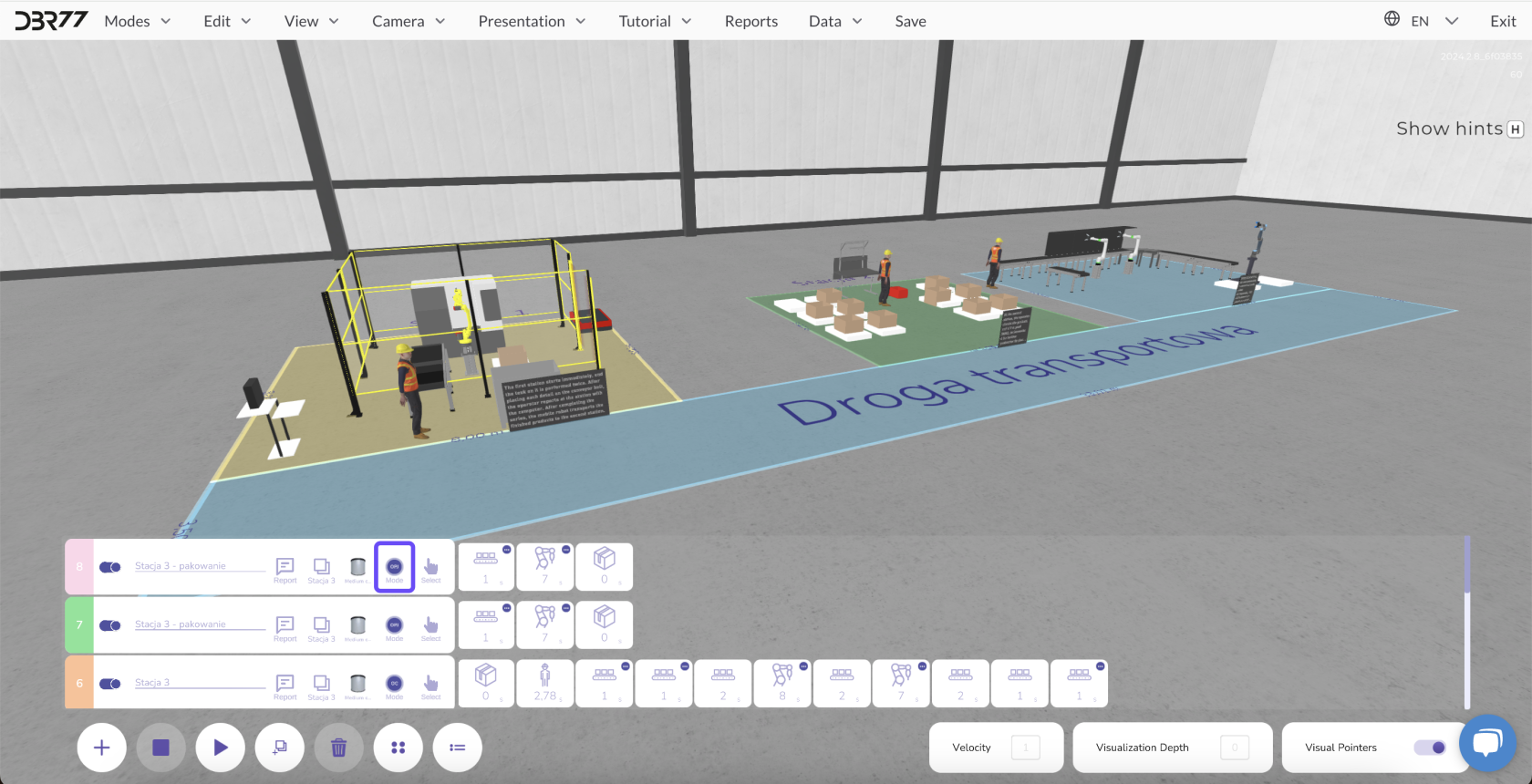
Start Methods
In the 3D studio, there are several ways to start animation lines, customizable to meet production needs.
Here are the three main methods:
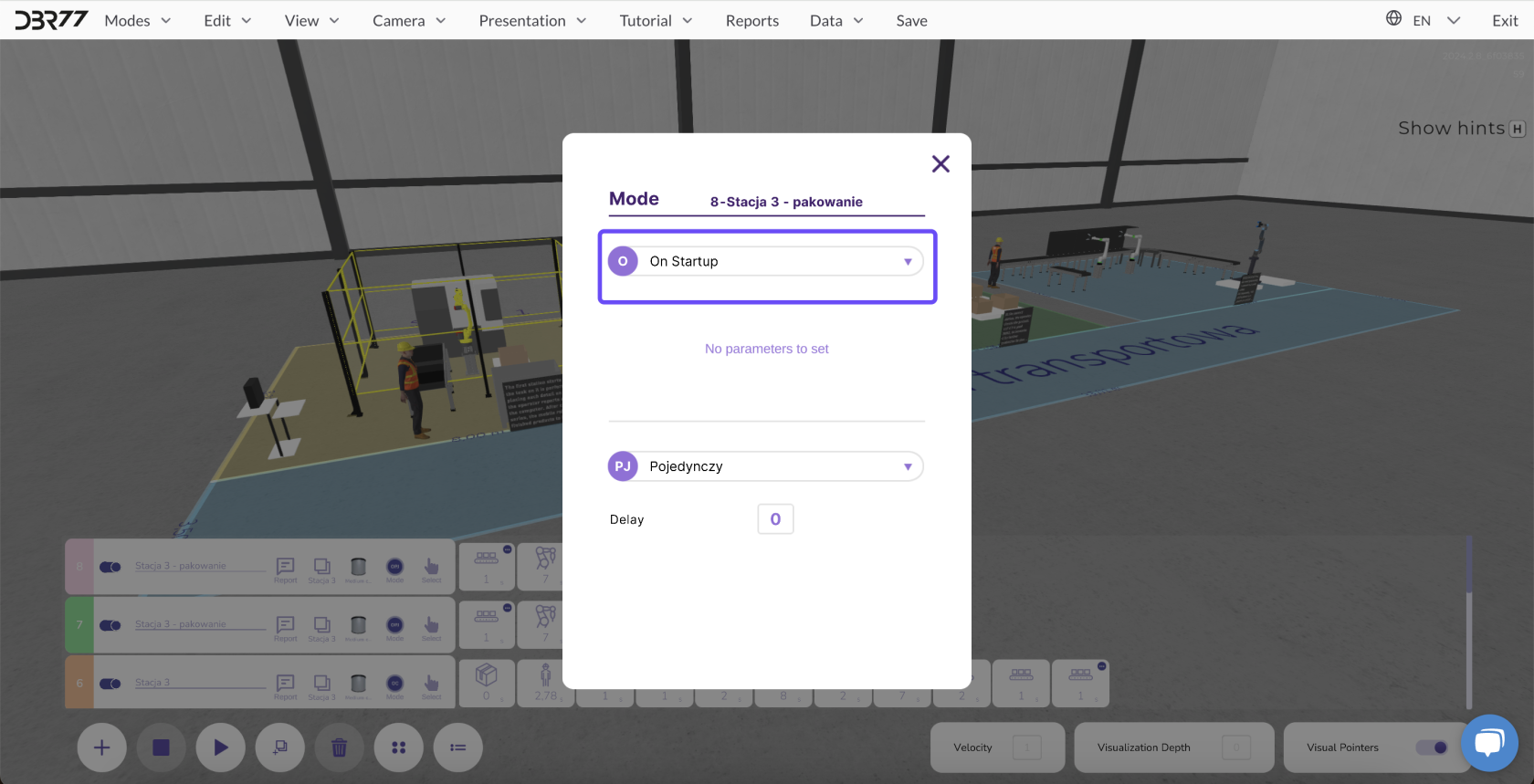
1. Immediate Start
- Description: After clicking the "Play" button, the entire animation line starts immediately, and all elements begin executing their programmed tasks without delay.
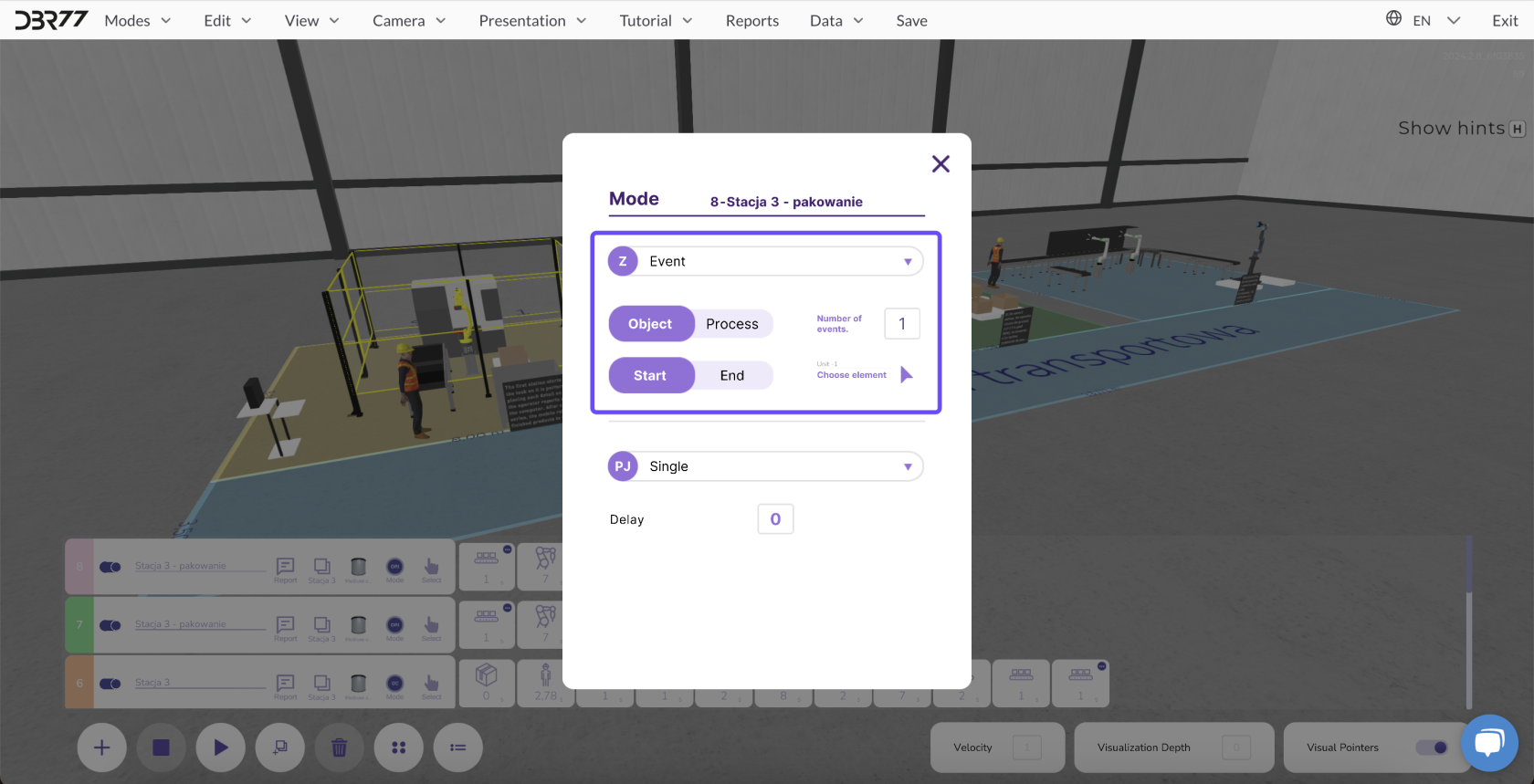
2. Event-Driven Start
Description: Events are conditions that define the start or end time of an object or process.
Defining Events:
- Select an element that controls the start or end of another object or process.
- Specify after how many events the selected animation line should start.
Example:
The next line starts only after the previous one has completed its tasks.
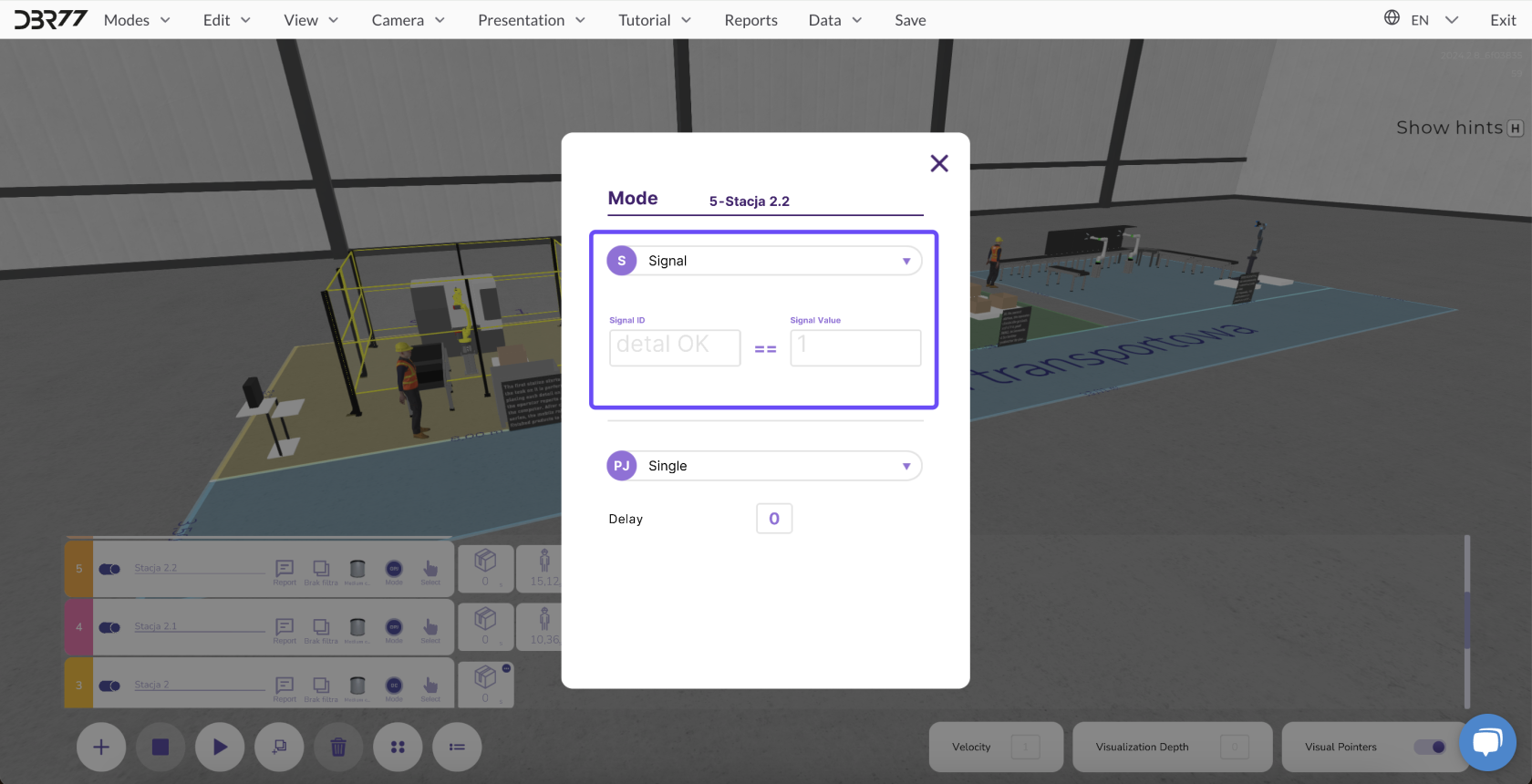
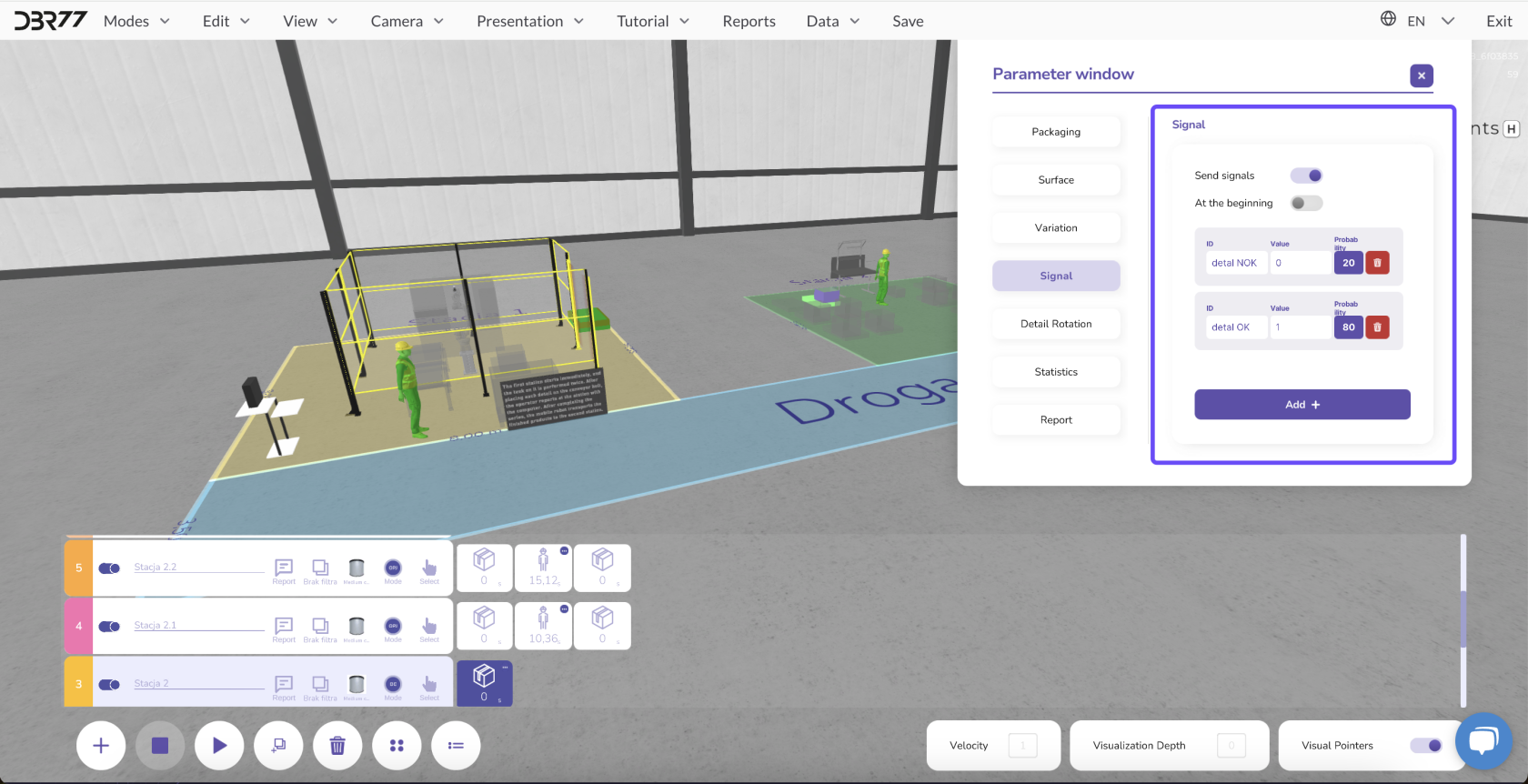
3. Signal from a Specific Element
-
Description: Signals determine whether a specific element meets the conditions to activate the next animation line.
Signal Functionality:
-
Example: In a quality control system:
- If an element passes inspection ("OK"), a signal with a value of 1 is sent, activating the next line.
- If an element fails inspection ("Defective"), a signal with a value of 0 is sent, blocking the next line. The defective element is redirected elsewhere instead of being further processed.
Defining Probabilities:
- Specify how often a certain signal should occur.
- Example: Set a 75% probability for elements passing and 25% for defects to control the production process more effectively.
Summary
Each method allows for flexible control of animation lines in the 3D studio, enabling you to optimize workflows to meet the specific requirements of your production process.

No Comments